{ Java Algorithms } Algorithms
Today’s Algorithm Concepts : HashMap, HashSet, Prefix
HashMap
- Map 인터페이스를 구현한 함수
- Key 값의 hashCode를 index로 Araay에 값을 저장 및 조회 = 빠른 검색속도
- key 값은 중복이 되지 않고, value 값은 허용
- 키에 대한 해시 값을 사용하여 값을 저장하고 조회하며, 키-값 쌍의 개수에 따라 동적으로 크기가 증가하는 associate array = Map = Dictionary = Symbol Table
- Dictionary? An abstract class that stores key-value pairs.
HashMap<Integer, String> nameMap = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
nameMap.put(1, "Nicollas");
nameMap.put(2, "Hyukjoo");
nameMap.put(3, "Jaydon");
nameMap.put(2, "Rachel");
System.out.println(nameMap); // Rachel will be printed
key 값은 중복 X, value 값은 중복 O. key 값이 중복된다면 최종 2에 저장된 value 는 “Rachel”로 나중에 입력된 key의 value로 덮어 씌어 진다.
HashMap: 반복문으로 데이터 꺼내오기
- Iterator; 컬렉션에 저장되어 있는 데이터를 읽어오는 방법 중 하나
public interface Iterator {
boolean hasNext(); // 읽어 올 요소가 남아있는지 확인
Object next(); // 다음데이터를 반환
void remove(); // next()로 읽어 온 요소를 삭제
}
...
// 1. hasNext -> 2. next -> 3. remove
map.put(1, "Nicollas");
map.put(2, "Hyukjoo");
map.put(3, "Jaydon");
map.put(2, "Rachel");
Iterator<Integer> keySetIterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (keySetIterator.hasNext()) {
Integer key = keySetIterator.next();
System.out.println("key: " + key + " value: " + map.get(key));
}
...
----- Output -----
key: 1 value: Nicollas
key: 2 value: Rachel
key: 3 value: Jaydon
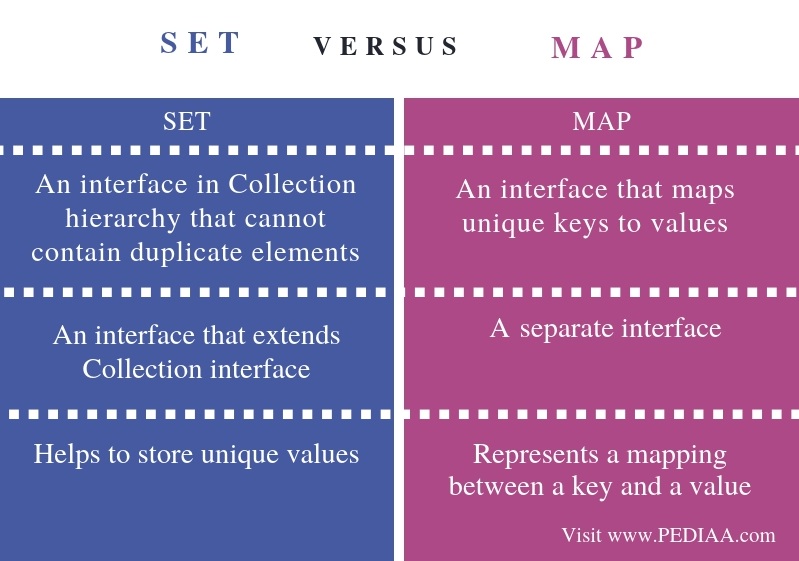
HashSet
- Map vs Set
Prefix
- A technique used to calculate the sum of elements in a specified slice of an array
- 나열된 수의 누적된 합
Where will Prefix Sum be used?
- a 에서 b 의 구간 합을 요구하는 문제가 많이 들어왔을 때, 시간 복잡도를 낮추기 위하여 사용
- 모든 입력마다 구간합을 일일히 구해주는 경우에는 구간의 길이가 M이라고 하면 매 구간합을 구할 때 마다 O(M)이라는 시간이 걸리게 된다. 즉, N개의 구간 에 대해 구간의 길이가 M인 구간합을 구하는 경우 O(NM)의 시간이 걸리는 것
- 특정 구간까지의 구간합을 모두 구해 놓기만 한다면(O(M)) 구간 합을 구하는 연산 자체는 O(1)의 시간이면 구할 수 있기 때문에 결론적으로 O(N + M)의 시간 복잡도
- 누적 합을 구하고, 그 누적합을 이용하여 주어진 구간의 합을 구하는 로직
Source code 1 (from leetcode)
public int[] runningSum(int[] nums) {
int[] ans = new int[nums.length];
ans[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < ans.length; i++) {
ans[i] = ans[i-1] + nums[i];
}
return ans;
}
Source code 2 (from leetcode)
public int pivotIndex(int[] nums) {
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
total += nums[i];
}
int leftSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (leftSum == total - leftSum - nums[i]) {
return i;
}
leftSum += nums[i];
}
return -1;
}